NCUIH Requests the Administration of Children and Families Host Urban Confer with UIOs Regarding the Tribal Maternal, Infant, and Early Childhood Home Visiting Program
On January 27, 2023, the National Council of Urban Indian Health submitted comments to the Administration for Children and Families (ACF) in response to their December 20, 2022 request for comment on review of the Tribal Maternal, Infant, and Early Childhood Home Visiting Program (Tribal MIECHV) Guidance for Submitting Reports to the Secretary of the Office of Management and Budget (OMB). The Tribal MIECHV Program provides grants to tribal organizations and urban Indian organizations (UIOs) to develop, implement, and evaluate home visiting programs in American Indian and Alaska Native (AI/AN) communities.
Recommendations
NCUIH made the following recommendations to ACF in response to the request for comments:
- NCUIH requested that ACF host an Urban Confer with UIO leaders to discuss the Tribal MIECHV program.
- NCUIH recommended that ACF work with its colleagues at IHS to host and facilitate an Urban Confer on the annual reporting requirements for Tribal MIECHV grantees.
- Given the substantial increase in the set-aside for the Tribal NCUIH further recommends that ACF consider broadening the scope of this Urban Confer to engage with UIOs on the Tribal MIECHV program generally.
- This will provide ACF a forum in which to work with UIOs to ensure that they are participating in this program to the greatest extent possible and that urban Native communities are being served as Congress intended.
Background
Under the ACF, the MIECHV Program supports pregnant people and parents with young children who live in communities that face greater risks and barriers to achieving positive maternal and child health outcomes. The Tribal MIECHV program is funded by a six percent set-aside from the larger MIECHV program. The Tribal MIECHV program aims to support the development of happy, healthy, and successful AI/AN children and families through a coordinated home visiting strategy that addresses critical maternal and child health, development, early learning, family support, and child abuse and neglect prevention needs. It also implements high-quality, culturally relevant, evidence-based home visiting programs in AI/AN communities and expands the evidence base around home visiting interventions with Native populations.
Urban Native Maternal and Child Health Disparities
Native people have endured a tragic history of forced removal from their homelands throughout eras of colonization and US expansion. Formally dating back to the 1800s, forced removal included the loss of ancestral homelands, children taken from their parents and placed into government boarding schools, and policy aimed at integrating Native people into US cities, each resulting in traditional and cultural deprivation. This migration into cities has resulted in urban Indians experiencing more unemployment and homelessness compared to the general population, lower levels of educational achievement, higher rates of morbidity and mortality and a loss of traditional and cultural connection. Urban Indian women have considerably lower rates of prenatal care and higher rates of infant mortality than their reservation counterparts within the same state. While UIOs provide critical health and social services, the safety net available to those living on reservations is often not matched in urban environments. Recognizing the health disparities experienced by urban Indians, MIECHV legislation allows Tribal MIECHV funds to be awarded to UIOs to further support the health and social needs of Native people living in urban areas.
NCUIH’s Role
NCUIH has engaged in extensive policy work, including attending Congressional meetings and joining sign-on letters with coalition partners, in support of reauthorizing the MIECHV program and doubling the Tribal set-aside. NCUIH was pleased that Congress reauthorized the Tribal MIECHV program and increased the funding level. The Tribal MIECHV program helps improve the lives of AI/AN children and families and NCUIH looks forward to more UIOs becoming grantees and working with ACF to support the development of happy, healthy, and successful Native children and families no matter where they live.

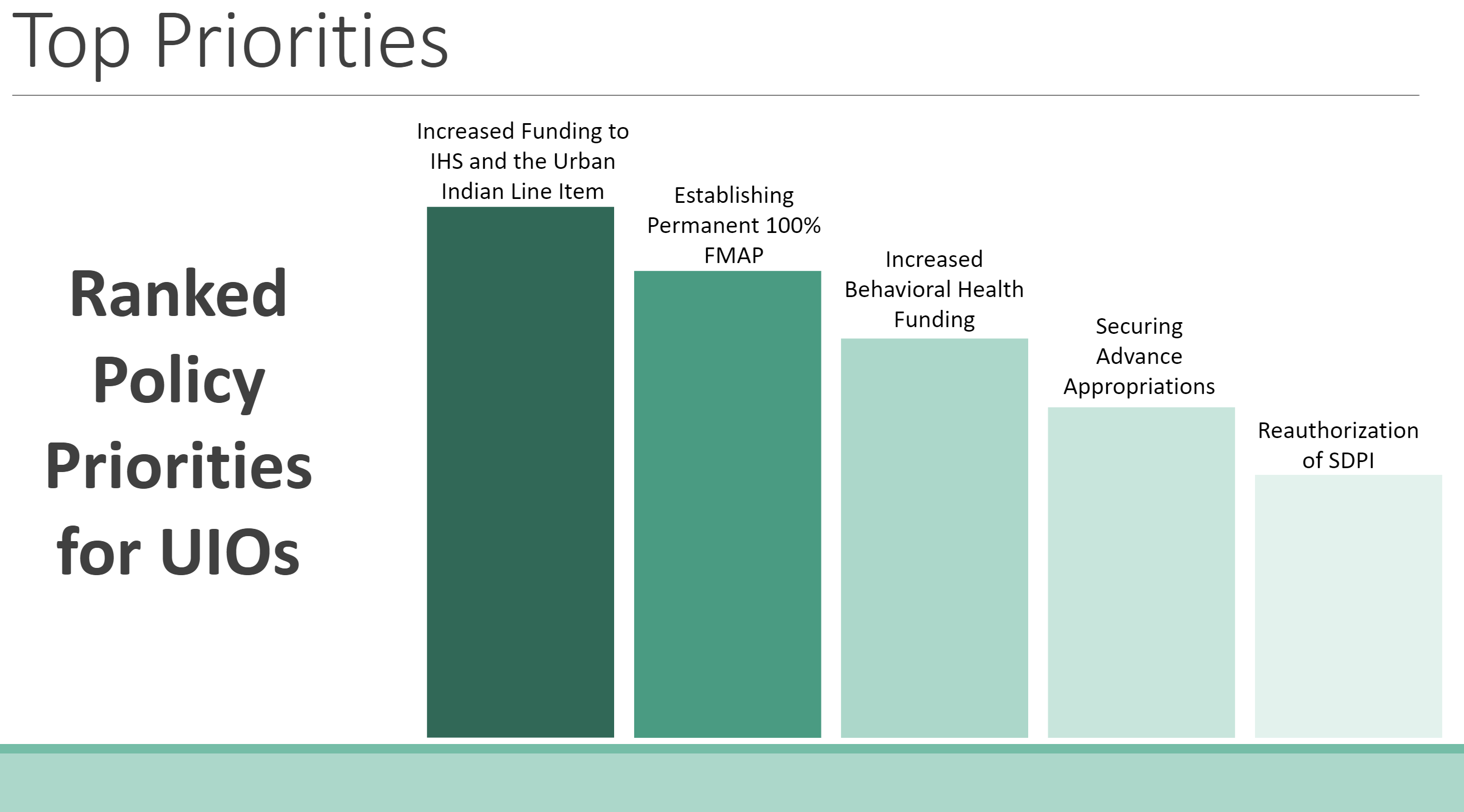
 The National Council of Urban Indian Health (NCUIH) is pleased to announce the release of its
The National Council of Urban Indian Health (NCUIH) is pleased to announce the release of its 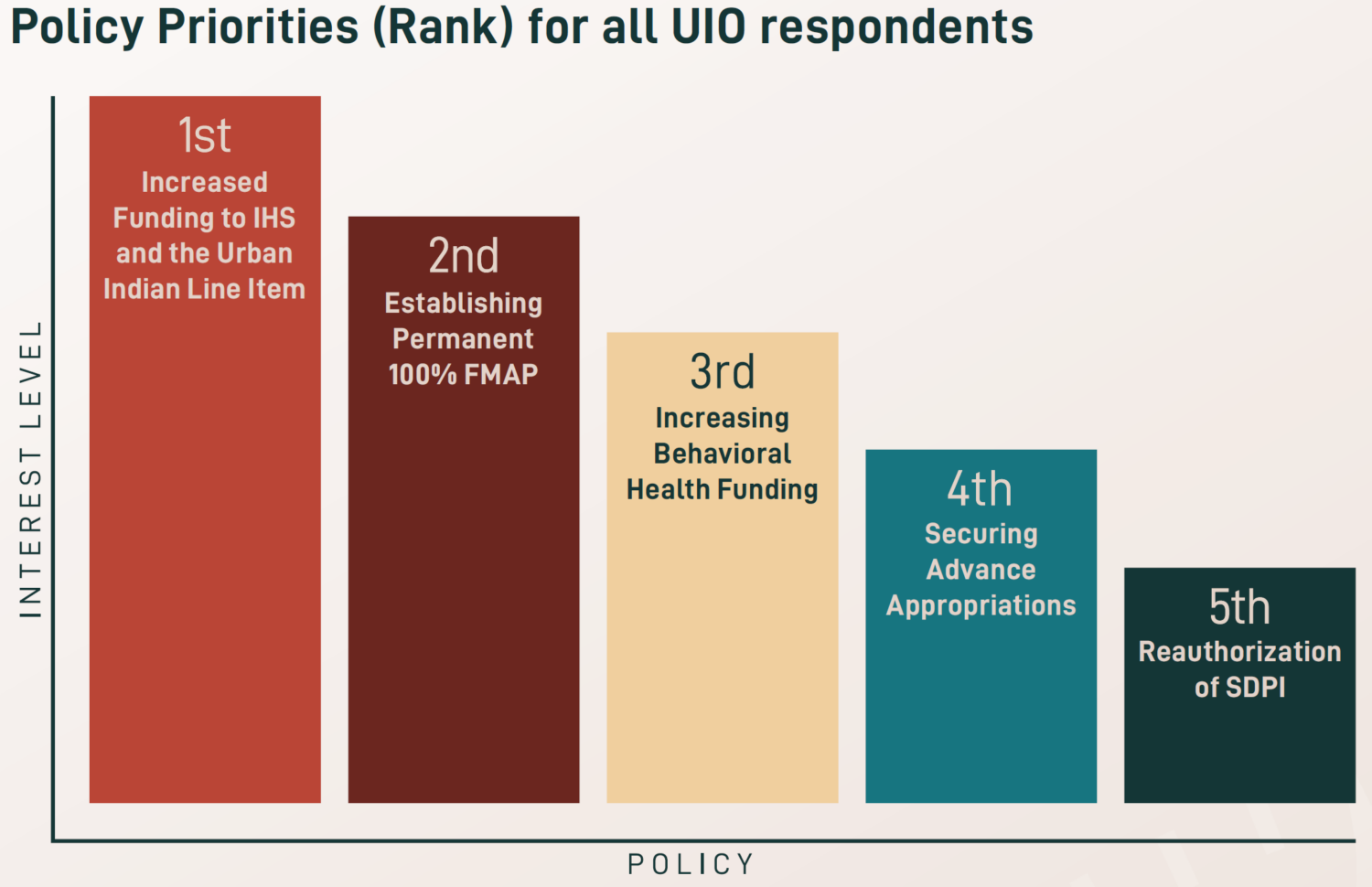 After the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, newfound priorities were identified for 2023, including workforce development and retention, increased funding for traditional healing, and expanded access to care and telehealth services. Existing priorities also remain a key focus across UIOs, especially increasing funding amounts for the urban Indian health line item and IHS, maintaining advance appropriations for IHS, establishing permanent 100% Federal Medical Assistance Percentage (FMAP) for UIOs, reauthorizing the Special Diabetes Program for Indians (SDPI), and increasing behavioral health funding.
After the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, newfound priorities were identified for 2023, including workforce development and retention, increased funding for traditional healing, and expanded access to care and telehealth services. Existing priorities also remain a key focus across UIOs, especially increasing funding amounts for the urban Indian health line item and IHS, maintaining advance appropriations for IHS, establishing permanent 100% Federal Medical Assistance Percentage (FMAP) for UIOs, reauthorizing the Special Diabetes Program for Indians (SDPI), and increasing behavioral health funding.