August Policy Updates: Focus Groups, Traditional Foods Report, FY25 Funding and more!
🔍 Policy Priorities: Join September UIO focus groups to shape 2025 policies.
🍲🌾New NCUIH Resource: NCUIH Infographic on Traditional Food Programs at UIOs.
🏦 Report Update: NCUIH publishes a report on Medicaid Reimbursement at UIOs during the COVID-19 Pandemic.
📊 Appropriations Updates: FY25 bills advance with proposed increases to Indian Country programs; a Continuing Resolution might be needed post-September 30.
🇺🇸 NCUIH in Action: NCUIH represents UIOs at White House Voting Rights Convening.
📞 Advocacy: Advocating for the Urban Indian Health Parity Act and the Truth and Healing Commission bill.
✍🏽 Upcoming Comment Deadlines: September 6: IHS Health Information Technology (HIT) Modernization comments due; September 9: CMS Medicaid Four Walls Exemption feedback due; October 1: United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Dietary Guidelines comments due.
📅 Important Dates: Mark your calendars for upcoming meetings, conferences, and events.
Next Week: Focus Groups to Shape 2025 Policy Priorities

These sessions are an opportunity for UIO leaders and their staff to discuss your vital priorities that shape our advocacy efforts in 2025. We will host 5 individual sessions to allow UIO leaders and their staff from each UIO type to have unique discussions with NCUIH staff:
September 3
- 1:00-2:30 p.m. EST – Full Ambulatory
- 3:00-4:30 p.m. EST – Outpatient and Residential
September 4
- 1:00-2:30 p.m. EST – Limited Ambulatory
- 3:00-4:30 p.m. EST – Outreach and Referral
September 5
- 1:00-2:30 p.m. EST – Makeup Session
If you are unable to attend any of these dates, please email Policy@NCUIH.org to set up an individual session. We would love to hear from you!
NCUIH Resources: Report on Medicaid Reimbursement at UIOs during COVID-19 Pandemic and Infographic on Traditional Food Programs at UIOs

NCUIH’s Infographic “Analysis of Traditional Food Programs” complements NCUIH’s recently released report on Traditional Foods at UIOs and highlights:
- Importance of traditional foods in Native communities.
- Impact of colonization on traditional food practices.
- Overview of common programs at UIOs that can incorporate traditional foods: Special Diabetes Program for Indians (SDPI), Nutritional Counseling, Food Prescriptions, and Community Gardens.
- Access the Infographic here.
NCUIH’s report “Medicaid Reimbursement Rates at Urban Indian Organizations During the COVID-19 Pandemic” focuses on the impact of Medicaid reimbursement rates at UIOs during COVID-19. Despite UIOs providing additional services and growing programs to serve the urban Native community during COVID-19 pandemic, reimbursement rates did not significantly rise.
- Access the report here.
Appropriations Updates: Senate Advances 2025 Funding Bill, Protects Key Indian Country Programs

Senate Advances Labor-HHS Appropriations Bill:
On August 1, 2024, the Senate Appropriations Committee advanced their FY 2025 Labor, Health, and Human Services (LHHS) appropriations bill which proposes increased or maintained funding for key Indian Country programs.
- By the numbers: Includes $8 million for Improving Native American Cancer Outcomes, which would create an Initiative for Improving Native American Cancer Outcomes to be located at a National Cancer Institute-designated cancer center demonstrating strong partnerships with Tribes, Tribal Organizations, and UIOs;$24 million for the Good Health and Wellness in Indian Country program; and $23.67 million for Tribal Behavioral Health Grants.
- What’s Ahead: FY 2024 funding is set to end on September 30, 2024. If Congress cannot come to a funding agreement by that deadline, a Continuing Resolution will be needed to maintain funding levels at FY24 levels until an agreement is reached.
- Go deeper: Read NCUIH’s analysis of the bill.
Take Action to Support Mandatory Funding for IHS CSCs and 105(l) leases:
NCUIH sent out an action alert urging advocates to contact Congress to support mandatory funding for IHS Contract Support Costs (CSCs) and 105(l) lease funding.
-
Ways to advocate: Call or email your Representative, and post on social media using the template language provided in the action alert. Contact Congress.
NCUIH in Action: Engaging at White House Event on Native American Voting Rights
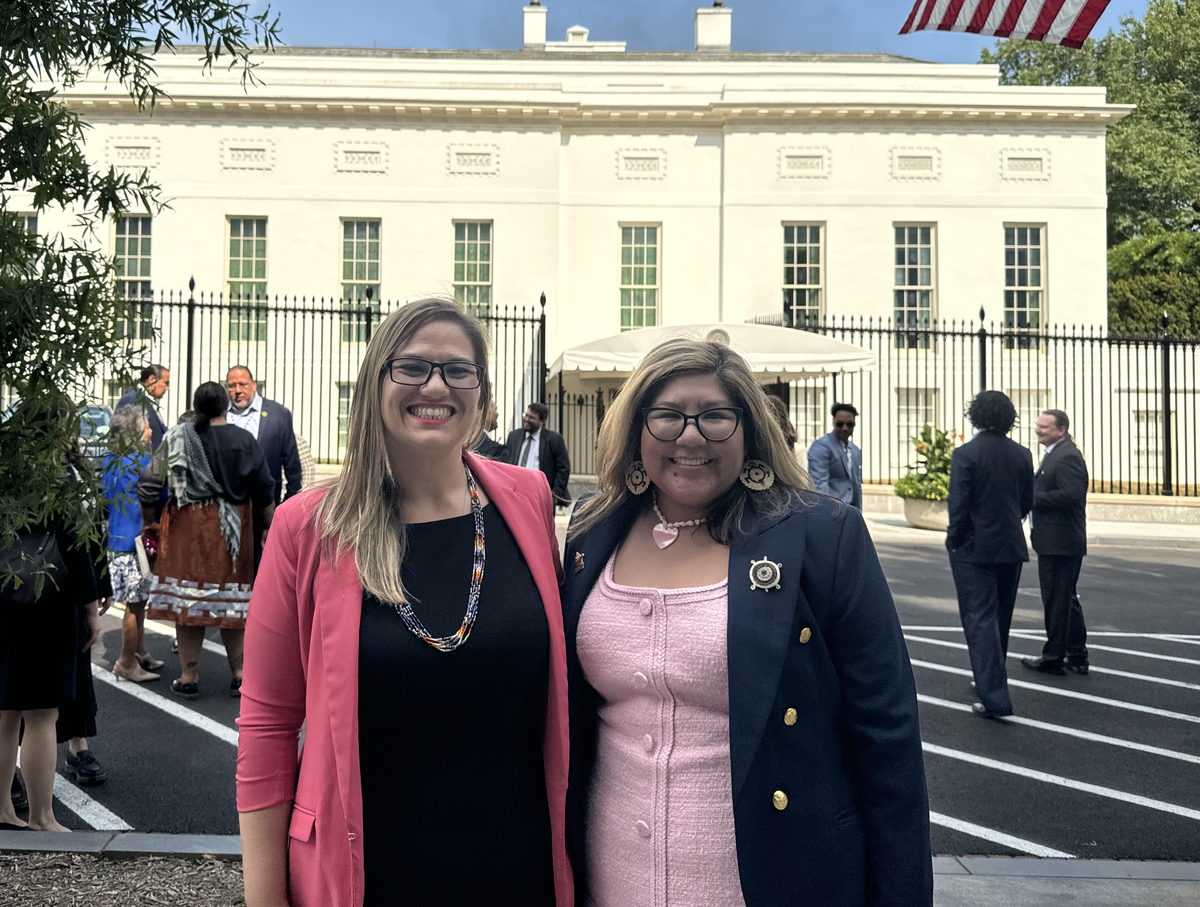

NCUIH CEO, Francys Crevier (Algonquin) and Executive Director of White House Initiative for Native Americans and Tribal Colleges and Universities, Naomi Miguel (Tohono O’odham).
On July 31, NCUIH CEO Francys Crevier attended the White House Convening on Native American Voting Rights. Ensuring every Native vote is heard is essential to our democracy & the well-being of our people. UIOs are at the forefront of this mission, promoting civic engagement & health equity.
What else?: The election is coming up, and NCUIH has created special resources for UIOs. Download Posters and Flyers
Legislative Updates: Addressing Federal Indian Boarding Schools, Audio-Only Telehealth Services, and 100% FMAP for UIOs

Two potential pathways for the Truth and Healing Commission on Indian Boarding School Policies Act of 2023 (S. 1723/H.R. 7227) bill to be passed:
- On July 8, 2024, the Senate bill was placed on the legislative calendar. The expectation is that the bill will pass the Senate.
- Additionally, Senators Brian Schatz (Hawaii- Chair of the Senate Committee on Indian Affairs) and Lisa Murkowski (Alaska – Vice-Chair) filed a bipartisan amendment attaching the bill to the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA), providing the bill with two potential pathways to be passed.
- The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) score for the House bill was released with $90 million authorized over FY24-FY2034, funded from unobligated ARPA (American Rescue Plan Act) IHS funding.
- The House bill is awaiting a committee report before being scheduled for a floor vote.
- Why it matters: the bill would establish a formal commission to investigate, document, and acknowledge past injustices of the federal government’s Indian Boarding School Policies.
On August 2, Rep. Teresa Leger Fernandez (D-NM-3) introduced the NCUIH-endorsed IHS Audio-Only Telehealth Bill, which would make permanent a COVID-19 Public Health Emergency temporary provision allowing audio-only telehealth services for Medicare beneficiaries receiving care through Indian health programs or UIOs.
- Why it matters: IHS, tribally operated facilities, and UIOs would benefit from continued reimbursement from Medicare for audio-only telehealth services as program budgets heavily depend upon third-party reimbursements.
- Go Deeper: Read more on NCUIH’s blog.
Recent update on 100% Federal Medical Assistance Percentage (FMAP) for UIO Medicaid Services:
NCUIH is working to advance legislation by the end of 2024 for 100% FMAP for UIO Medicaid services.
Next Steps: Congress is currently in recess until September 9 and will only have three weeks of work before the session ends on September 27. During this short session, the focus is expected to be on addressing the government funding that expires on September 30, making it unlikely that other legislation will advance before the election. However, the lame-duck session—the period between the November election and the start of the new Congress—will be crucial for passing key legislation. Reports suggest that Congress could move on an end-of-year package that includes health extenders. NCUIH will continue to advocate for the inclusion of 100% FMAP in any legislation Congress considers during this time.
What UIOs Can Do:
- If UIOs would like to write a letter or meet with their Member of Congress to support this legislation, NCUIH is available to assist. Email policy@ncuih.org.
- Reminder: UIOs can still work with their states to improve Medicaid reimbursement rates even without 100% FMAP.
NCUIH Advocates for Full Funding to Meet Indian Country Needs and UIO and Tribal Engagement in Recommendations to the White House

On August 9, NCUIH submitted comments to the White House regarding Executive Order (EO) 14112 Section 4(a): Assessing Additional Funding to Better Live up to the Trust Responsibility.
Go deeper: NCUIH recommended that forthcoming White House guidance to agencies working to calculate the unmet scope of the trust responsibility direct them to: capture the full level of federal funding need to meet the trust obligation for health to all of Indian Country and engage with UIOs through urban confer and continue to seek tribal feedback.
Upcoming Federal Comment Opportunities: Syphilis Outbreak, HIT Modernization, Medicaid Four Walls Exemption, and Dietary Guidelines
September 5: HHS Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health (OASH) – Syphilis and Congenital Syphilis Outbreak
OASH seeks information from Indian Country about possible HHS actions that may support efforts to reduce the number of syphilis and congenital syphilis cases among American Indians and Alaska Natives. Specifically, they seek comments on the following questions:
- What are your top three priorities for addressing the syphilis and congenital syphilis epidemic in Indian country?
- What are the top three changes that HHS could implement to reduce the cases of syphilis and congenital syphilis in your communities?
- What successful models or innovations have you implemented that could be adapted and scaled by other communities?
What’s next: The deadline for written comments is September 5, 2024, and can be submitted to STI@hhs.gov, using the following subject line: “Tribal Consultation.”
September 6: IHS – Health IT Modernization Multi-Tenant Domain Considerations.
IHS seeks to better understand how to enhance the benefits and address challenges with the new Electronic Health Record (EHR) system, now called PATH (Patients at the Heart). IHS specifically seeks comments on the following questions:
- What can IHS do to increase the value proposition for urban partners to participate in PATH EHR (Electronic Health Record)?
- What challenges and risks might your facilities face when transitioning to PATH EHR?
- What should IHS consider when preparing end users to operate within a shared EHR environment with a single patient record?
What’s Next: The deadline for written comments is September 6, 2024, and can be submitted to consultation@ihs.gov or urbanconfer@ihs.gov, using the following subject line: ” Health IT Modernization.”
There will also be a joint IHS Tribal Consultation/Urban Confer session on November 7, 2024, 1:30-3 PM ET, on HIT Modernization Site Readiness and Training. This will be a hybrid event at IHS Headquarters in Rockville, MD. Register here.
September 9: CMS – Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS) Proposed Rule
- CMS hosted an All Tribes Consultation Webinar on August 8, 2024.
- CMS is requesting information related to a Tribal Technical Advisory Group (TTAG) request to apply the IHS Medicare encounter rate to all outpatient Tribal clinics for Medicare services.
- CMS also proposes to establish a permanent exception to the Medicaid clinic services benefit four walls requirement for IHS and Tribal clinics, and, at state option, for behavioral health clinics and clinics located in rural areas.
What’s Next: The deadline for written comments is September 9, 2024, and can be submitted electronically at https://www.regulations.gov (follow the “Submit a comment” instructions), or by mail to the following address: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Department of Health and Human Services, Attention: CMS-1809-P, P.O. Box 8010, Baltimore, MD 21244-8010.
October 1 – United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Dietary Guidelines for America
- USDA is seeking public comment as the 2025 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee conducts its scientific review process. Learn more here.
What’s next: Written comments are due October 1, 2024, and can be submitted online (preferred method) at the Federal eRulemaking Portal, or by mail to Janet M. de Jesus, MS, RD, HHS/OASH Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (ODPHP), 1101 Wootton Parkway, Suite 420, Rockville, MD 20852. All submissions received must include the agency name and Docket OASH-2022-0021.
Upcoming Events and Important Dates

Sept. 5: Association of American Indian Physicians (AAIP) Conference in Salt Lake City, UT. NCUIH will be presenting its reports on Traditional Healing. Register here.
Sept. 10-12: IHS Direct Service Tribes Advisory Committee (DSTAC) 4th Quarter Meeting. Location TBD. Visit IHS website for more information.
Sept. 10-12: HHS Secretary’s Tribal Advisory Committee (STAC) – Northwest Portland Area
Sept. 10: Medicare, Medicaid and Health Reform Policy Committee (MMPC) Monthly Meeting
Sept, 17-18: Tribal Leaders Diabetes Committee (TLDC) Quarterly Meeting in Washington, D.C (hybrid). Link to join meeting on September 17. Link to join meeting on September 18.
ICYMI: Recent IHS Tribal and Urban Leader Letters, IHS Strategic Plan Recommendations, and Budget Insights

Recent Dear Tribal and Urban Leader Letters (DTLL/DULL)
IHS wrote to share tools to address climate change, associated health risks, and strategies to address environmental justice:
- U.S. Climate Resilience Toolkit
- CDC’s Heat & Health Tracker
- Federal Flood Standard Support Tool
- FEMA’s National Risk Index
- EPA’s EJ Screen: Environmental Justice Screening and Mapping Tool
Important Events:
July 22-23: IHS Tribal Self-Governance Advisory Committee (TSGAC) Meeting
- IHS representatives reported that reclassifying CSC and 105 (l) leases to mandatory funding would protect the entire IHS budget.
TSGAC’s recommendations for improving the IHS strategic plan:
- Develop a public strategic plan scorecard
- Develop evaluation or monitoring mechanism
- Tribal consultation requirements in the plan’s objectives/activities
July 25: IHS FY 2026-2027 Tribal Budget Formulation Planning and Evaluation Meeting
- The FY25 President’s Budget provides an additional $1 billion annually in FY26 and FY27 to fully address the 2023 estimated backlog of essential maintenance, alteration, and repair (BMAR) for IHS and tribal facilities, and to account for anticipated growth in the BMAR through FY 2026.
- IHS staff stated that the FY 2025 House Bill includes a $115 million decrease to the Electronic Health Record (EHR) Modernization Project. This decrease is likely due to the Fiscal Responsibility Act (FRA).
One last thing, check out this upcoming funding opportunity:
Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA) New Access Points (NAPs)
- HRSA announces that applications to establish NAPs are now open to expand access to affordable, high-quality primary health care, including mental health and substance use disorder services, for underserved communities and populations. HRSA will only be able to make awards for this Notice of Funding Opportunity if Congress appropriates additional funds for the Health Center Program in FY 2025. HRSA-funded health centers operate more than 15,000 service sites nationwide. If Congress appropriates additional funding in FY 2025, these NAPs will expand the number of health centers in the HRSA Health Center Program and help HRSA-funded health centers open new locations. NAP applicants may be currently funded health centers, look-alikes, or new organizations (those not yet part of the Health Center Program).
- Applications are due in Grants.gov on August 30, 2024, and in HRSA’s Electronic Handbooks on September 30, 2024 (Apply).



