President Biden Continues to Demonstrate Strong Commitment to Urban Indians, Proposes Over 50% Increase for Urban Indian Health for FY 2023
The FY 2023 budget request includes $113 million for urban Indian health, a 53% increase over the FY 2022 enacted amount and mandatory appropriations for IHS.
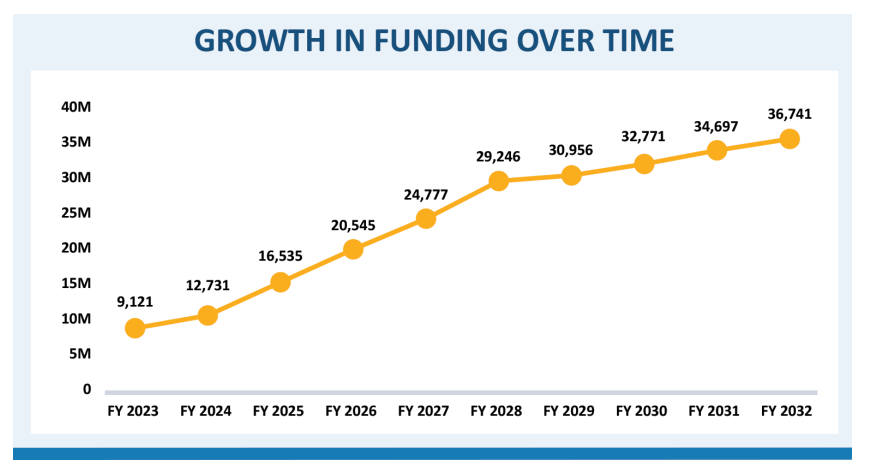
On April 25, 2022, the Indian Health Service (IHS) published their Fiscal Year (FY) 2023 Congressional Justification with the full details of the President’s Budget, which includes $112.5 million for Urban Indian Health— a 53.2% increase above the FY 2022 enacted amount of $73.4 million. According to the IHS Congressional Justification, “This funding increase could support an estimated 1,072,935 health care, outreach, and referral services to Urban Indian users in FY 2023.” The President’s proposal included a total of $127.3 billion in discretionary funding for the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) and, for the first time ever, $9.3 billion in mandatory funding for IHS for the first year, which includes $9.1 billion in proposed law funding and $147 million in current law funding for the Special Diabetes Program for Indians (SDPI). The budget proposes increased funding for IHS each year over ten years, building to $36.7 billion in FY 2032, to keep pace with population growth, inflation, and healthcare costs.
“The Indian Health System and urban Indian health have long been severely underfunded: only 1% of the Indian health budget goes to urban Indian health despite more than 70% of American Indians and Alaska Natives residing in urban areas. We are grateful for the President’s inclusion of $113 million for urban Indian health in FY 2023. President Biden has shown a strong commitment to urban Indian communities, and we recognize this Administration’s dedication to improving outcomes for all of Indian Country. As the final amount still falls well short of fully funding the Indian Health Service to properly provide health care services for all Natives in the United States to meet the trust responsibility, we will continue to push Congress to provide all the resources necessary to protect the lives of the entire Native population, regardless of where they live,”
– Francys Crevier (Algonquin), CEO, NCUIH
Line Item |
FY21
|
FY22 Enacted |
FY23 TBFWG Request |
FY23
|
| Urban Indian Health | $62,684,000 | $73,424,000 | $949,900,000 | $112,514,000 |
| Indian Health Service | $6,236,279,000 | $6,630,986,000 | $49,800,000,000 | $9,100,000,000 |
The National Council of Urban Indian Health requested full funding for urban Indian health for FY 2023 at $949.9 million and at least $49.8 billion for IHS in accordance with the Tribal Budget Formulation Workgroup (TBFWG) recommendations. The marked increase for FY23 is a result of Tribal leaders, over several decades, providing budget recommendations to phase in funding increases over 10-12 years to address growing health disparities that have largely been ignored. The Congressional Justification states, “IHS recognizes that we must continue to work in consultation with Tribes and confer with Urban Indian Organizations, and with our partners in Congress, to ensure the budget is structured and implemented correctly with the resources identified over the next 10 years.”
Background and Advocacy
On March 28, 2022, President Biden released his budget request for Fiscal Year FY 2023, pending the more detailed IHS budget request released April 25, which includes specifics on the IHS budget request, including the funding recommendations for urban Indian health.
- IHS FY 2023 Congressional Justification
- President’s FY 2023 Budget
- NCUIH Analysis of President’s FY 2023 Budget
On April 5, 2022, NCUIH President-Elect and CEO of the Indian Health Center of Santa Clara Valley, Sonya Tetnowski (Makah Tribe), testified before and submitted public witness written testimony to the House Appropriations Subcommittee on Interior, Environment, and Related Agencies regarding FY 2023 funding for Urban Indian Organizations (UIOs). NCUIH requested $49.8 billion for the Indian Health Service and $949.9 million for Urban Indian Health for FY 2023 as requested by the TBFWG, Advance appropriations for IHS, and support of mandatory funding for IHS including UIOs.
- NCUIH Appropriations Testimony
- Watch Ms. Tetnowski’s Opening Remarks
- Watch Full Appropriations Hearing
- NCUIH Press Release on FY 2023 Appropriations Hearing
NCUIH recently worked closely with Representatives Gallego and Grijalva on leading a Congressional letter to the House Committee on Appropriations in support of increasing the urban Indian health line item for FY 2023. The letter has bipartisan support and calls for the highest possible funding for Urban Indian Health up to the TBFWG’s recommendation of $949.9 million and advanced appropriations for IHS until such time that authorizers move IHS to mandatory spending.
- Gallego and Rep. Grijalva’s Letter
- NCUIH Toolkit: Contact Congress to Increase Funding for Urban Indian Health TODAY
Next Steps
The Appropriations Committees will review the President’s Budget for consideration as they craft their bills for FY 2023. NCUIH will continue to work with the Biden Administration and Congress to push for full funding of urban Indian health in FY 2023.