Advancing Sexual Health Programs at Urban Indian Organizations: Best Practices, Challenges, and Solutions
This blog post explores best practices for improving STI programming, the challenges Urban Indian Organizations (UIOs) encounter, and effective strategies to enhance sexual health outcomes.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) represent a significant public health concern, particularly among underserved populations, which include urban American Indian and Alaska Native (AI/AN) communities.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), AI/AN communities experience higher rates of STIs compared to other racial and ethnic groups, with chlamydia rates nearly 1.5 times the national average and gonorrhea rates approximately 4.6 times higher than the national average.1
AI/AN communities continue to face a significant increase in syphilis rates. The rate of primary and secondary syphilis among AI/AN individuals rose from 21.1 cases per 100,000 people in 2019 to 58.2 cases per 100,000 people in 2023. Additionally, congenital syphilis rates in this population increased from approximately 200 cases per 100,000 live births in 2019 to 680.8 cases per 100,000 live births in 2023.2
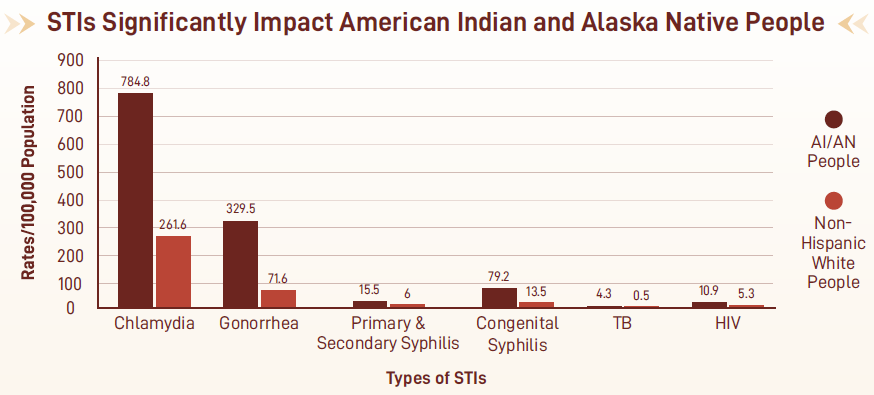
Figure 1: Rates of (STIs) and other infectious diseases per 100,000 among American Indian and Alaska Native (AI/AN) people, compared to non-Hispanic White people.
UIOs serve as essential providers of sexual health services, addressing the unique health care needs of their special population and resources. Through these efforts, UIOs have made meaningful STI prevention and care advancements and contributed to improved health outcomes. Continued support to enhance the STI service capacity of UIOs is vital for sustaining these efforts and addressing broader systemic challenges.
Additional NCUIH resources for this topic include:
- HIV/STIs Syndemic Resource Guide: A comprehensive toolkit designed to provide essential resources for UIOs.
- Barriers and Needs to Urban Indian Sexual Health Services Provision: A Mixed Methods Approach: A report summarizing the results of a questionnaire distributed to UIOs to explore STI service capacities at UIOs.
- STI Service Guidance for Indian Health Care Providers: A flyer designed with an overview of best practices for providers and a quick look at AI/AN STI/HIV data.
Best Practices for Effective STI Programs
Community-tailored, inclusive, and accessible care is fundamental to improving STI prevention and treatment in urban AI/AN communities. UIOs have successfully adopted the following approaches:
Community-Based Programs
Programs that reflect the cultural values and traditions of AI/AN communities are far more effective in engaging patients and fostering trust. Successful practices include:
- Providing community-informed health education that incorporates traditional healing practices and ceremonies.
- Promoting healthy, body-positive conversations about sexuality that are inclusive of two-spirit (2S) and LGBTQ+ community members.
Expanding Accessibility
Ensuring that STI services are widely available and easy to access is essential. UIOs can enhance their offerings by:
- Providing self-collection test kits for patients who prefer privacy.
- Expanding expedited partner therapy (EPT) services, enabling partners of patients with STIs to receive treatment without separate clinic visits.
- Offering extragenital screenings for infections in areas beyond genital testing, like throat and rectal swabs.
Collaborations and Resource Sharing
Partnerships with state health departments, Tribal entities, and other organizations are key to scaling services and sharing knowledge. Programs like the Health Resources and Services Administration’s (HRSA’s) 340B Drug Pricing Program can help UIOs access affordable medications, while initiatives such as “I Want the Kit” provide essential testing supplies at no cost.
Comprehensive Staff Training
Training health care providers is vital for delivering high-quality, patient-centered care. Staff should:
- Stay updated on STI treatment and testing guidelines, including clinical laboratory improvement amendments (CLIA)-waived tests.
- Create a welcoming environment for patients to discuss sensitive sexual health topics openly.
Challenges and Strategies for Improving Sexual Health Outcomes at UIOs
In 2023, NCUIH surveyed 15 UIOs to understand the status and impacts of their STI prevention and care service provision to patients and community members. Below is an overview of the challenges expressed by UIOs in the survey and potential strategies for overcoming these challenges.
Challenges Faced by UIOs
While UIOs are uniquely positioned to improve sexual health outcomes for urban AI/AN populations, they often operate under significant constraints. The most common barriers include:
Funding Shortages
Many UIOs report insufficient funding to support critical tools, testing materials, and treatment resources. Nearly half of the surveyed UIOs identified funding as a major challenge.
Staffing and Training Gaps
Limited staffing and inadequate training can result in inconsistent care delivery. UIOs may struggle to meet patient demand or implement new services without enough trained personnel.
Stigma and Misinformation
Stigma surrounding STIs can discourage patients from seeking care or discussing sexual health openly. This stigma is compounded by misinformation, making it harder for UIOs to reach at-risk individuals effectively.
Policy and Administrative Barriers
Many UIOs lack access to key state and federal funding opportunities, such as Section 318 of the Public Health Service Act. Inconsistent policies across states can further complicate billing, reporting, and service delivery.
Effective Strategies for Overcoming Challenges
Despite these obstacles, UIOs are finding innovative ways to improve STI prevention and treatment in their communities. Below are some strategies that have proven effective:
Streamlining Patient Access
- Offering walk-in STI testing and same-day appointments to remove barriers to timely care.
- Hosting community events such as health fairs or educational workshops in schools and cultural centers can increase awareness and engagement.
Investing in Workforce Development
- Providing ongoing staff training to ensure people are well-equipped to deliver compassionate, high quality care.
- Offer training programs focused on inclusive communication and community competency to help address stigma and create safer spaces for patients.
Leveraging Technology
- Robust electronic health record (EHR) systems to help track patient data, streamline reporting, and improve follow-up care.
- Digital outreach through social media and other platforms to disseminate educational materials and promote available services.
Building Strong Community Partnerships
- Collaborating with local health departments, Tribal Epidemiology Centers, and other stakeholders to enhance service coordination and resource sharing.
- Involving community members in program development ensures that services are relevant and meet patient needs.
NCUIH’s Role in Supporting UIOs
NCUIH provides essential support to UIOs through technical assistance, training, research, and advocacy. These efforts focus on:
- Securing funding to expand health promotion and treatment services for urban AI/AN communities.
- Providing Tribal relevant training programs and educational materials.
- Advocating for policy changes that address systemic inequities in access to sexual health care.
- Conducting to support STI prevention, treatment, and improved health outcomes for urban AI/AN communities.
- Offering to enhance UIO capacity in delivering effective STI prevention and care services.
By fostering collaboration and empowering UIOs, NCUIH helps ensure that urban AI/AN populations receive the care they need to lead healthier lives.
Moving Forward
UIOs are indispensable in addressing sexual health disparities among urban AI/AN communities. By adopting best practices, tackling barriers, and implementing innovative strategies, they can continue to make a meaningful impact.
With the support of NCUIH and , UIOs can expand access to high-quality, community-competent care and improve sexual health outcomes for the communities they serve. Together, we can create a future where everyone has the resources and support to thrive.
CDC Disclaimer: This publication was supported by grant number 5 NU50CK000601-04-00 funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Its contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the CDC or the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).





